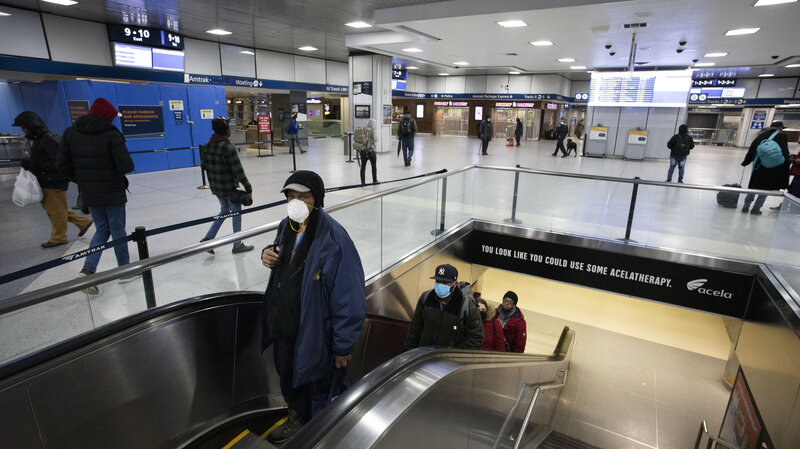
Cuomo Orders All Hospitals To Add Beds As New York Confirms 20,000 Coronavirus Cases
New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo says that in his state — the U.S. epicenter for the coronavirus — the wave of new cases is still going up. Here, commuters wearing masks pass through New York City's Penn Station on Monday.
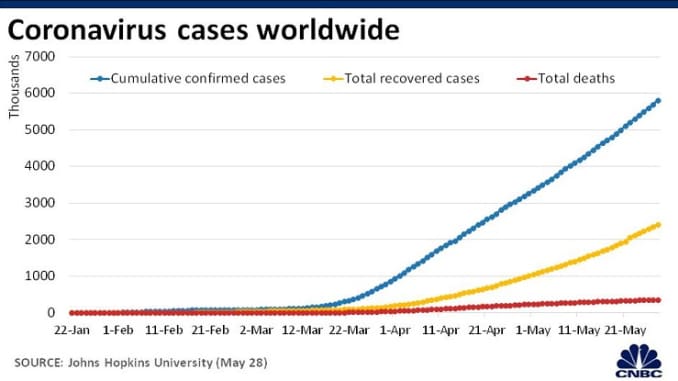
Global coronavirus cases cross 350,000, death toll passes 15,000 as pandemic takes hold
PUBLISHED MON, MAR 23 20208:46 AM EDT UPDATED 2 HOURS AGO
William Feuer@WILLFOIA
KEY POINTS
- COVID-19 has now infected more than 350,536 people, according to Johns Hopkins University, and killed at least 15,328 people.
- Global cases have more than doubled in the past week, according to the World Health Organization, and worldwide deaths have nearly tripled.
- Outside of China, where the virus emerged in December, Italy has the most confirmed cases with nearly 60,000.
WHO launches global megatrial of the four most promising coronavirus treatments
By Kai Kupferschmidt, Jon CohenMar. 22, 2020 , 3:28 PM
Could any of these drugs hold the key to saving coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients from serious harm or death? On Friday, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced a large global trial, called SOLIDARITY, to find out whether any can treat infections with the new coronavirus for the dangerous respiratory disease. It’s an unprecedented effort—an all-out, coordinated push to collect robust scientific data rapidly during a pandemic. The study, which could include many thousands of patients in dozens of countries, has been designed to be as simple as possible so that even hospitals overwhelmed by an onslaught of COVID-19 patients can participate.
With about 15% of COVID-19 patients suffering from severe disease and hospitals being overwhelmed, treatments are desperately needed. So rather than coming up with compounds from scratch that may take years to develop and test, researchers and public health agencies are looking to repurpose drugs already approved for other diseases and known to be largely safe. They’re also looking at unapproved drugs that have performed well in animal studies with the other two deadly coronaviruses, which cause severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).
Drugs that slow or kill the novel coronavirus, called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), could save the lives of severely ill patients, but might also be given prophylactically to protect health care workers and others at high risk of infection. Treatments may also reduce the time patients spend in intensive care units, freeing critical hospital beds.
Scientists have suggested dozens of existing compounds for testing, but WHO is focusing on what it says are the four most promising therapies: an experimental antiviral compound called remdesivir; the malaria medications chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine; a combination of two HIV drugs, lopinavir and ritonavir; and that same combination plus interferon-beta, an immune system messenger that can help cripple viruses. Some data on their use in COVID-19 patients have already emerged—the HIV combo failed in a small study in China—but WHO believes a large trial with a greater variety of patients is warranted.
Enrolling subjects in SOLIDARITY will be easy. When a person with a confirmed case of COVID-19 is deemed eligible, the physician can enter the patient’s data into a WHO website, including any underlying condition that could change the course of the disease, such as diabetes or HIV infection. The participant has to sign an informed consent form that is scanned and sent to WHO electronically. After the physician states which drugs are available at his or her hospital, the website will randomize the patient to one of the drugs available or to the local standard care for COVID-19.
“After that, no more measurements or documentation are required,” says Ana Maria Henao-Restrepo, a medical officer at WHO’s Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals. Physicians will record the day the patient left the hospital or died, the duration of the hospital stay, and whether the patient required oxygen or ventilation, she says. “That’s all.”
The design is not double-blind, the gold standard in medical research, so there could be placebo effects from patients knowing they received a candidate drug. But WHO says it had to balance scientific rigor against speed. The idea for SOLIDARITY came up less than 2 weeks ago, Henao-Restrepo says, and the agency hopes to have supporting documentation and data management centers set up next week. “We are doing this in record time,” she says.
It will be important to get answers quickly, to try to find out what works and what doesn’t work. We think that randomized evidence is the best way to do that.
Ana Maria Henao-Restrepo, World Health Organization
Arthur Caplan, a bioethicist at New York University Langone Medical Center, says he likes the study’s design. “No one wants to tax the frontline caregiver who’s overwhelmed and taking risks anyway,” Caplan says. Hospitals that aren’t overburdened might be able to record more data on disease progression, for instance by following the level of virus in the body, Caplan suggests. But for public health, the simple outcomes WHO seeks to measure are the only relevant ones for now, says virologist Christian Drosten of the Charité University Hospital in Berlin: “We don’t really know enough about this disease to be sure what it means when the viral load decreases in the throat, for instance.”
On Sunday, INSERM, the French biomedical research agency, announced it will coordinate an add-on trial in Europe, named Discovery, that will follow WHO’s example and will include 3200 patients from at least seven countries, including 800 from France. That trial will test the same drugs, with the exception of chloroquine. Other countries or groups of hospitals could organize add-on studies as well, Heneo-Restrepo says. They are free to do additional measurements or observations, for instance on virology, blood gases, chemistry, and lung imaging. “While well-organized additional research studies of the natural history of the disease or of the effects of the trial treatments could well be valuable, they are not core requirements,” she says.
The list of drugs to test was first put together for WHO by a panel of scientists who have been assessing the evidence for candidate therapies since January, Heneo-Restrepo says. The group of selected drugs that had the highest likelihood of working, had the most safety data from previous use, and are likely to be available in supplies sufficient to treat substantial numbers of patients if the trial shows they work.
Here are the treatments that SOLIDARITY will test:
Remdesivir
The new coronavirus is giving this compound a second chance to shine. Originally developed by Gilead Sciences to combat Ebola and related viruses, remdesivir shuts down viral replication by inhibiting a key viral enzyme, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
Researchers tested remdesivir last year during the Ebola outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, along with three other treatments. It did not show any effect. (Two others did.) But the enzyme it targets is similar in other viruses, and in 2017 researchers at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, showed in test tube and animal studies that the drug can inhibit the coronaviruses that cause SARS and MERS.
The first COVID-19 patient diagnosed in the United States—a young man in Snohomish county in Washington—was given remdesivir when his condition worsened; he improved the next day, according to a case report in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM). A Californian patient who received remdesivir—and who doctors thought might not survive—recovered as well.
Such evidence from individual cases doesn’t prove a drug is safe and effective. Still, from the drugs in the SOLIDARITY trial, “remdesivir has the best potential to be used in clinics” says Jiang Shibo of Fudan University, who has long worked on coronavirus therapeutics. Jiang particularly likes that high doses of the drug can likely be given without causing toxicities.
However, it may be much more potent if given early in an infection, like most other drugs, says Stanley Perlman, a coronavirus researcher at the University of Iowa. “What you really want to do is give a drug like that to people who walk in with mild symptoms,” he says. “And you can’t do that because it’s an [intravenous] drug, it’s expensive and 85 out of 100 people don’t need it.”
Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine
At a press conference on Friday, President Donald Trump called chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine a “game changer.” “I feel good about it,” Trump said. His remarks have led to a rush in demand for the decades-old antimalarials. (“It reminds me a little bit of the toilet paper phenomenon and everybody’s running to the store,” Caplan says.)
The WHO scientific panel designing SOLIDARITY had originally decided to leave the duo out of the trial, but had a change of heart at a meeting in Geneva on 13 March, because the drugs “received significant attention” in many countries, according to the report of a WHO working group that looked into the drugs’ potential. The widespread interested prompted “the need to examine emerging evidence to inform a decision on its potential role.”
The available data are thin. The drugs work by decreasing the acidity in endosomes, compartments inside cells that they use to ingest outside material and that some viruses can coopt to enter a cell. But the main entryway for SARS-CoV-2 is a different one, using its so-called spike protein to attach to a receptor on the surface of human cells. Studies in cell culture have suggested chloroquines have some activity against SARS-CoV-2, but the doses needed are usually high—and could cause serious toxicities.
Encouraging cell study results with chloroquines against two other viral diseases, dengue and chikungunya, didn’t pan out in people in randomized clinical trials. And nonhuman primates infected with chikungunya did worse when given chloroquine. “Researchers have tried this drug on virus after virus, and it never works out in humans. The dose needed is just too high,” says Susanne Herold, an expert on pulmonary infections at the University of Giessen.
Results from COVID-19 patients are murky. Chinese researchers who report treating more than 100 patients with chloroquine touted its benefits in a letter in BioScience, but the data underlying the claim have not been published. All in all, more than 20 COVID-19 studies in China used chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine, WHO notes, but their results have been hard to come by. “WHO is engaging with Chinese colleagues at the mission in Geneva and have received assurances of improved collaboration; however, no data has been shared regarding the chloroquine studies.”
Researchers in France have published a study in which they treated 20 COVID-19 patients with hydroxychloroquine. They concluded that the drug significantly reduced viral load in nasal swabs. But it was not a randomized controlled trial and it didn’t report clinical outcomes such as deaths. In guidance published on Friday, the U.S. Society of Critical Care Medicine said “there is insufficient evidence to issue a recommendation on the use of chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine in critically ill adults with COVID-19.”
Hydroxychloroquine, in particular, might do more harm than good. The drug has a variety of side effects and can in rare cases harm the heart. Because people with heart conditions are at higher risk of severe COVID-19, that is a concern, says David Smith, an infectious disease physician at the University of California, San Diego. “This is a warning signal, but we still need to do the trial,” he says. What’s more, a rush to use the drug for COVID-19 might make it harder for the people who need it to treat their rheumatoid arthritis or malaria.
Ritonavir/lopinavir
This combination drug, sold under the brand name Kaletra, was approved in the United States in 2000 to treat HIV infections. Abbott Laboratories developed lopinavir specifically to inhibit the protease of HIV, an important enzyme that cleaves a long protein chain into peptides during the assembly of new viruses. Because lopinavir is quickly broken down in the human body by our own proteases, it is given with low levels of ritonavir, another protease inhibitor, that lets lopinavir persist longer.
The combination can inhibit the protease of other viruses as well, specifically coronaviruses. It has shown efficacy in marmosets infected with the MERS virus, and has also been tested in SARS and MERS patients, though results from those trials are ambiguous.
The first trial with COVD-19 was not encouraging, however. Doctors in Wuhan, China, gave 199 patients two pills of lopinavir/ritonavir twice a day plus standard care, or standard care alone. There was no significant difference between the groups, they reported in NEJM on 15 March. But the authors caution that patients were very ill—more than one-fifth of them died—and so the treatment may have been given too late to help. Although the drug is generally safe it may interact with drugs usually given to severely ill patients, and doctors have warned it could cause significant liver damage.
Ritonavir/lopinavir and interferon-beta
SOLIDARITY will also have an arm that combines the two antivirals with interferon-beta, a molecule involved in regulating inflammation in the body that has also shown an effect in marmosets infected with MERS. A combination of the three drugs is now being tested in MERS patients in Saudi Arabia in the first randomized controlled trial for that disease.
But the use of interferon-beta on patients with severe COVID-19 might be risky, Herold says. “If it is given late in the disease it could easily lead to worse tissue damage instead of helping patients,” she cautions.
Thousands of patients
The design of the SOLIDARITY trial can change at any time. A global data safety monitoring board will look at interim results at regular intervals and decide whether any member of the quartet has a clear effect, or whether one can be dropped because it clearly does not. Several other drugs, including the influenza drug favipiravir, produced by Japan’s Toyama Chemical, may be added to the trial.
To get robust results from the study, several thousands of patients will likely have to be recruited, Henao-Restrepo says. Argentina, Iran, South Africa, and several other non-European countries have already signed up. WHO is also hoping to do a prevention trial to test drugs that might protect health care workers from infection, using the same basic protocol, Henao-Restrepo says.
The trial’s European counterpart, Discovery, will recruit patients from France, Spain, the United Kingdom, Germany, and the Benelux countries, according to an INSERM press release today. The trial will be led Florence Ader, an infectious diseases researcher at the University Hospital Center in Lyon.
Doing rigorous clinical research during an outbreak is always a challenge, Henao-Restrepo says, but it’s the best way to make headway against the virus: “It will be important to get answers quickly, to try to find out what works and what doesn’t work. We think that randomized evidence is the best way to do that.”
Posted in: HealthCoronavirus
doi:10.1126/science.abb8497
| Location | Confirmed cases | Cases per 1M people | Recovered | Deaths |
|---|
 Worldwide Worldwide | 372,147 | 52.81 | 101,069 | 16,310 |
 China China | 81,093 | 60.53 | 72,703 | 3,270 |
 Italy Italy | 63,928 | 1059.86 | 7,432 | 6,078 |
 United States United States | 42,161 | 135.31 | 187 | 508 |
 Spain Spain | 33,089 | 708.04 | 3,355 | 2,206 |
 Germany Germany | 28,914 | 347.74 | 453 | 118 |
 Iran Iran | 23,049 | 277.09 | 8,376 | 1,812 |
 France France | 19,856 | 296.26 | 2,200 | 860 |
 South Korea South Korea | 8,961 | 173.30 | 3,166 | 111 |
 Switzerland Switzerland | 8,249 | 962.53 | 131 | 107 |
 United Kingdom United Kingdom | 6,650 | 98.45 | 140 | 335 |
 Netherlands Netherlands | 4,768 | 273.63 | — | 214 |
 Austria Austria | 3,924 | 440.77 | — | 21 |
 Belgium Belgium | 3,743 | 325.03 | 350 | 88 |
 Norway Norway | 2,570 | 478.80 | — | 10 |
 Portugal Portugal | 2,060 | 200.46 | 14 | 23 |
 Sweden Sweden | 2,046 | 198.00 | 16 | 25 |
 Canada Canada | 2,020 | 53.44 | 18 | 24 |
 Australia Australia | 1,717 | 67.33 | 88 | 7 |
 Brazil Brazil | 1,629 | 8.10 | 2 | 25 |
 Denmark Denmark | 1,572 | 280.58 | — | 24 |
 Malaysia Malaysia | 1,518 | 46.32 | 159 | 14 |
 Israel Israel | 1,238 | 136.04 | 37 | 1 |
 Czechia Czechia | 1,236 | 116.06 | 6 | 1 |
 Turkey Turkey | 1,236 | 15.07 | 0 | 30 |
 Japan Japan | 1,101 | 8.61 | 235 | 41 |
 Ecuador Ecuador | 981 | 59.87 | 3 | 18 |
 Ireland Ireland | 906 | 184.09 | 5 | 4 |
 Luxembourg Luxembourg | 875 | 1425.33 | 6 | 8 |
 Pakistan Pakistan | 875 | 4.88 | 6 | 6 |
 Chile Chile | 746 | 42.45 | 11 | 1 |
 Thailand Thailand | 721 | 10.47 | 52 | 1 |
 Finland Finland | 700 | 126.78 | 10 | 1 |
 Greece Greece | 695 | 64.54 | 19 | 17 |
 Poland Poland | 692 | 18.03 | 1 | 8 |
 Iceland Iceland | 588 | 1614.23 | 51 | 1 |
 Indonesia Indonesia | 579 | 2.35 | 30 | 49 |
 Romania Romania | 576 | 29.69 | 73 | 6 |
 Saudi Arabia Saudi Arabia | 511 | 14.93 | 18 | 0 |
 Singapore Singapore | 509 | 90.27 | 152 | 2 |
 Qatar Qatar | 501 | 189.65 | 37 | 0 |
 India India | 468 | 0.36 | 34 | 9 |
 Philippines Philippines | 462 | 4.87 | 18 | 33 |
 Slovenia Slovenia | 442 | 211.07 | — | 3 |
 Russia Russia | 438 | 3.04 | 17 | 0 |
 South Africa South Africa | 402 | 6.84 | 2 | 0 |
 Bahrain Bahrain | 377 | 264.53 | 164 | 2 |
 Peru Peru | 363 | 11.06 | 1 | 5 |
 Hong Kong Hong Kong | 356 | 50.34 | 101 | 4 |
 Estonia Estonia | 352 | 264.99 | 4 | 0 |
 Egypt Egypt | 327 | 3.57 | 56 | 14 |
 Mexico Mexico | 316 | 2.61 | 4 | 2 |
 Croatia Croatia | 315 | 77.28 | 5 | 0 |
 Panama Panama | 313 | 77.59 | 1 | 3 |
 Lebanon Lebanon | 267 | 44.45 | 8 | 4 |
 Argentina Argentina | 266 | 5.92 | 27 | 4 |
 Iraq Iraq | 266 | 7.15 | 62 | 23 |
 Serbia Serbia | 249 | 34.29 | 2 | 3 |
 Dominican Republic Dominican Republic | 245 | 22.82 | 0 | 3 |
 Colombia Colombia | 235 | 4.87 | 3 | 2 |
 Algeria Algeria | 201 | 4.67 | 65 | 17 |
 United Arab Emirates United Arab Emirates | 198 | 20.63 | 41 | 2 |
 Taiwan Taiwan | 195 | 8.20 | 29 | 2 |
 Armenia Armenia | 194 | 66.33 | 2 | 0 |
 Bulgaria Bulgaria | 190 | 27.14 | 3 | 3 |
 Kuwait Kuwait | 189 | 40.89 | 30 | 0 |
 Slovakia Slovakia | 185 | 33.94 | 7 | 0 |
 Latvia Latvia | 180 | 93.75 | 1 | 0 |
 San Marino San Marino | 175 | 5248.32 | 4 | 20 |
 Hungary Hungary | 167 | 17.09 | 21 | 8 |
 Lithuania Lithuania | 154 | 55.11 | 1 | 1 |
 North Macedonia North Macedonia | 136 | 65.47 | 1 | 2 |
 Uruguay Uruguay | 135 | 39.20 | 0 | 0 |
 Costa Rica Costa Rica | 134 | 27.59 | 2 | 2 |
 Morocco Morocco | 134 | 3.77 | 3 | 4 |
 Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina | 128 | 36.45 | 2 | 1 |
 Vietnam Vietnam | 122 | 1.35 | 17 | 0 |
 Andorra Andorra | 112 | 1470.26 | 1 | 1 |
 Jordan Jordan | 112 | 10.76 | 1 | 0 |
 Malta Malta | 107 | 216.79 | 2 | 0 |
 Albania Albania | 104 | 36.15 | 3 | 4 |
 New Zealand New Zealand | 102 | 20.48 | 0 | 0 |
 Burkina Faso Burkina Faso | 99 | 4.92 | 5 | 4 |
 Cyprus Cyprus | 95 | 81.19 | 3 | 1 |
 Moldova Moldova | 94 | 35.05 | 2 | 1 |
 Brunei Brunei | 91 | 205.70 | 2 | 0 |
 Sri Lanka Sri Lanka | 91 | 4.20 | 3 | 0 |
 Tunisia Tunisia | 89 | 7.59 | 1 | 3 |
 Cambodia Cambodia | 86 | 5.63 | 2 | 0 |
 Belarus Belarus | 81 | 8.53 | 22 | 0 |
 Venezuela Venezuela | 77 | 2.63 | 15 | 0 |
 Ukraine Ukraine | 73 | 1.74 | 1 | 3 |
 Azerbaijan Azerbaijan | 72 | 7.18 | 10 | 1 |
 Senegal Senegal | 67 | 4.35 | 5 | 0 |
 Oman Oman | 66 | 14.92 | 17 | 0 |
 Kazakhstan Kazakhstan | 62 | 3.36 | 0 | 0 |
 Georgia Georgia | 61 | 16.38 | 8 | 0 |
 Palestine Palestine | 59 | 11.68 | 17 | 0 |
 Cameroon Cameroon | 56 | 2.39 | 2 | 0 |
 Trinidad and Tobago Trinidad and Tobago | 50 | 36.66 | 0 | 0 |
 Liechtenstein Liechtenstein | 46 | 1193.04 | 0 | 0 |
 Uzbekistan Uzbekistan | 46 | 1.36 | 0 | 0 |
 Afghanistan Afghanistan | 40 | 1.24 | 1 | 1 |
 Democratic Republic of the Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo | 36 | 0.53 | 0 | 2 |
 Nigeria Nigeria | 36 | 0.21 | 2 | 1 |
 Cuba Cuba | 35 | 3.12 | 0 | 1 |
 Bangladesh Bangladesh | 33 | 0.20 | 3 | 3 |
 Kosovo Kosovo | 31 | 17.12 | 0 | 0 |
 Bolivia Bolivia | 27 | 2.36 | 0 | 0 |
 Honduras Honduras | 27 | 2.96 | 0 | 0 |
 Côte d'Ivoire Côte d'Ivoire | 25 | 1.05 | 1 | 0 |
 Ghana Ghana | 24 | 0.77 | 0 | 1 |
 Macao Macao | 24 | 43.19 | 10 | 0 |
 Mauritius Mauritius | 24 | 18.96 | 0 | 2 |
 Monaco Monaco | 23 | 600.52 | 1 | 0 |
 Montenegro Montenegro | 22 | 34.85 | 0 | 1 |
 Paraguay Paraguay | 22 | 3.08 | 0 | 1 |
 Guernsey Guernsey | 20 | 305.00 | 0 | 0 |
 Guatemala Guatemala | 19 | 1.10 | 0 | 1 |
 Jamaica Jamaica | 19 | 6.57 | 2 | 1 |
 Rwanda Rwanda | 19 | 1.69 | 0 | 0 |
 Togo Togo | 18 | 2.26 | 0 | 0 |
 Barbados Barbados | 17 | 62.06 | 0 | 0 |
 Jersey Jersey | 16 | 163.50 | 0 | 0 |
 Kenya Kenya | 16 | 0.34 | 0 | 0 |
 Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan | 14 | 2.19 | 0 | 0 |
 Maldives Maldives | 13 | 33.12 | 3 | 0 |
 Madagascar Madagascar | 12 | 0.48 | 0 | 0 |
 Tanzania Tanzania | 12 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 |
 Ethiopia Ethiopia | 11 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 |
 Mongolia Mongolia | 10 | 3.05 | 0 | 0 |
 Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea | 9 | 7.37 | 0 | 0 |
 Seychelles Seychelles | 7 | 74.29 | 0 | 0 |
 Gabon Gabon | 5 | 2.53 | 0 | 1 |
 Guyana Guyana | 5 | 6.36 | 0 | 1 |
| Isle of Man | 5 | 60.00 | 0 | 0 |
 Suriname Suriname | 5 | 8.95 | 0 | 0 |
 Eswatini Eswatini | 4 | 3.52 | 0 | 0 |
 Guinea Guinea | 4 | 0.32 | 1 | 0 |
 The Bahamas The Bahamas | 4 | 10.22 | 0 | 0 |
 Cape Verde Cape Verde | 3 | 5.56 | 0 | 0 |
 Central African Republic Central African Republic | 3 | 0.65 | 0 | 0 |
 El Salvador El Salvador | 3 | 0.47 | 0 | 0 |
 Fiji Fiji | 3 | 3.24 | 0 | 0 |
 Liberia Liberia | 3 | 0.62 | 0 | 0 |
 Namibia Namibia | 3 | 1.15 | 0 | 0 |
 Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo | 3 | 0.59 | 0 | 0 |
| U.S. Virgin Islands | 3 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Zambia Zambia | 3 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 |
 Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | 3 | 0.19 | 0 | 1 |
 Angola Angola | 2 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
 Benin Benin | 2 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 |
 Bhutan Bhutan | 2 | 2.70 | 0 | 0 |
 Haiti Haiti | 2 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 |
 Mauritania Mauritania | 2 | 0.47 | 0 | 0 |
 Nepal Nepal | 2 | 0.07 | 1 | 0 |
 Nicaragua Nicaragua | 2 | 0.32 | 0 | 0 |
 Niger Niger | 2 | 0.10 | 0 | 0 |
 Saint Lucia Saint Lucia | 2 | 11.24 | 0 | 0 |
 Sudan Sudan | 2 | 0.05 | 0 | 1 |
 The Gambia The Gambia | 2 | 0.97 | 0 | 1 |
 Antigua and Barbuda Antigua and Barbuda | 1 | 9.90 | 0 | 0 |
 Belize Belize | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Chad Chad | 1 | 0.07 | 0 | 0 |
 Djibouti Djibouti | 1 | 1.13 | 0 | 0 |
 Dominica Dominica | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Eritrea Eritrea | 1 | 0.17 | 0 | 0 |
 Grenada Grenada | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Mozambique Mozambique | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea | 1 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 |
 Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 1 | 9.12 | 0 | 0 |
 Somalia Somalia | 1 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 |
 Syria Syria | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Timor-Leste Timor-Leste | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
 Uganda Uganda | 1 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 |
 Vatican City Vatican City | 1 | — | 0 | 0 |
| American Samoa | 0 | — | 0 | 0 |
| Northern Mariana Islands | 0 | — | 0 | 0 |
| | | | |




